Biochemistry
|
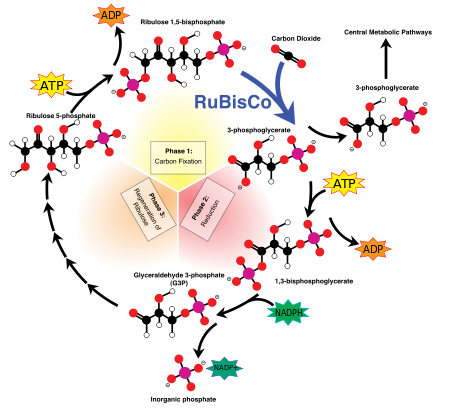
Plant biochemistry is the study of the chemical processes used by plants. Some of these processes are used in their primary metabolism like the photosynthetic Calvin cycle and crassulacean acid metabolism. Others make specialised materials like the cellulose and lignin used to build their bodies, and secondary products like resins and aroma compounds.
Plants and various other groups of photosynthetic eukaryotes collectively known as "algae" have unique organelles known as chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are thought to be descended from cyanobacteria that formed endosymbiotic relationships with ancient plant and algal ancestors. Chloroplasts and cyanobacteria contain the blue-green pigment chlorophyll a. Chlorophyll a (as well as its plant and green algal-specific cousin chlorophyll b) absorbs light in the blue-violet and orange/red parts of the spectrum while reflecting and transmitting the green light that we see as the characteristic colour of these organisms. The energy in the red and blue light that these pigments absorb is used by chloroplasts to make energy-rich carbon compounds from carbon dioxide and water by oxygenic photosynthesis, a process that generates molecular oxygen (O2) as a by-product. |
|